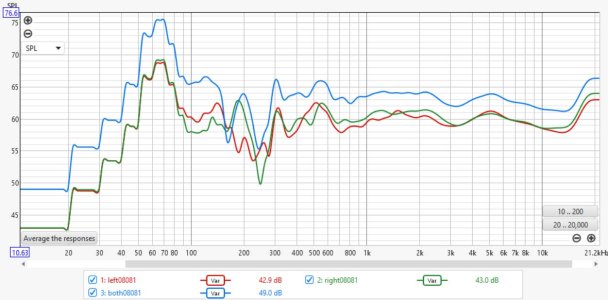
I've kept very quiet so far (as you might or might have not noticed

) because that first measurement didn't make any sense.
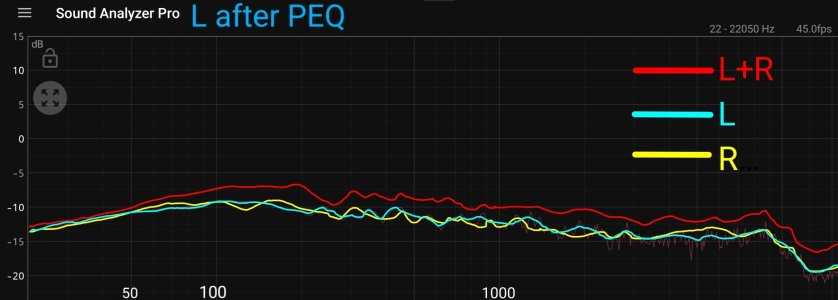
For lower frequencies one would expect ~6 dB gain for two speakers vs. one speaker because these sources have a high correlation at low frequencies. For higher frequencies there is little correlation, so the gain should be ~3 dB. That's exactly what the new measurement shows in my view.
Now, the concept of correlated sources isn't too popular a topic in the Hi-Fi world, but it's well known in acoustics in general and (hopefully) by audio professionals. There are a couple of ways to think about it to get a grasp (unless you already have it). Let me start with a typical and not too technical example.
- Imagine a violinist in a room playing just one note with as constant a level as possible for a human being. We and our microphone are in the same room, at some distance.
This will create a certain sound pressure level (SPL) in this room and in particular in our listening position. Reflected sound from the walls will contribute to the overall SPL, of course. There will be a slight variation with time but we can measure an average SPL and the deviation from that average will be small, because we are listening to an experienced musician.
- Now, a second violinist will enter the room, playing the exactly same note, standing close to the first violinist.
Question: Will the resulting sound in our listening position be louder than before?
Answer: Yes, it will.
Question: Will it be "twice as loud" as before?
Answer: No, it won't. While both violinists have be playing the same note, the sound pressure wave from both instruments will not be exactly identical at each point in time. Sometimes the will be very similar and mostly in phase, sometimes not so much, but on average the sound will still be louder, of course.
- The violinists went home, but we managed to do a close up mic recording of the single violinist. We put a speaker in the original position of the violin and replay that recording at exactly the same absolute level the violin did create.
Question: Will the resulting sound in our listening position be as loud as when the single violinist was playing before?
Answer: Yes, at least mostly. It depends on the directivity of the loudspeaker and the fidelity of our recording, but if both are good, the SPL will be about the same.
- Finally, we place two loudspeakers in the position of the violinists, close to each other, but we feed both the exact same recording of the first violinist. Each loudspeaker on its own will emit the same SPL as before, if only one of them is switched on. But now we switch on both speakers simultaneously.
Question: Will the resulting sound in our listening position be louder than before?
Answer: Yes, it will.
Question: Will the resulting sound be as loud as that played by two violins?
Answer: Will it be louder or softer than two violinists playing?
Answer: It will be louder. Both speakers are reproducing the exactly same sound wave at every point in time. There is (about) 100% correlation between the sources, the signals are coherent.
Now on to the numbers.:
How much louder will two violins be than a single one? How much louder will two speakers be than a single speaker?
Coherent signals can be summed up directly, for incoherent sound sources we need to sum up the acoustical power.
Luckily, we don't have to do all that on our own, because the late
engineer and Tonmeister Eberhard Sengpiel left us with a whole bunch of useful calculators and fundamental articles on acoustics and recording technology. Luckily, his son Alexander (who is not a sound engineer) is dedicated to preserving his father's legacy, a truely invaluable source of information, so we can still take advantage.
Here's the calculator for coherent signals (correlated sources):
Total dB level adding of correlated coherent sound sources combining decibels or SPL sound pressure level audio logarithmic decibel scale loudspeaker add signal noise levels incoherent noncoherent - Eberhard Sengpiel sengpielaudio

sengpielaudio.com
And here's the calculator for incoherent signals (uncorrelated sources):
Total dB level adding of uncorrelated incoherent noncoherent sound sources signals combine sound levels two sources resultant level audio logarithmic decibel scale decibels or SPL sound pressure level add signal noise levels incoherent random phase acoustic - Eberhard Sengpiel sengpielaudio

sengpielaudio.com
For those who prefer to not follow these external links immediately: The SPL of two violins is ~3 dB higher than a single one.
The SPL of two speakers is ~6 dB higher than a single one.
But wait!
Didn't I just state that the two loudspeakers reproducing exactly the same signal are
coherent sources? Shouldn't the SPL be up by 6 dB all over the frequency range then?
No, not really. These two speakers can be seen as corellated only at low frequencies with long wavelengths. At higher frequencies and with both speakers spaced noticeably apart (compared to the wavelength) there are all kinds of different room reflections adding up. Those acoustic signals are no longer perfectly in phase (although the electrical signal is). The result is still louder than a single speaker playing, but due to room reflections with vastly differing run times to the microphone we no longer have two distinct correlated sources.
As a result the total SPL at higher frequencies with both speakers replaying the same signal is different from the SPL at low frequencies.
.

) because that first measurement didn't make any sense.
sengpielaudio.com
sengpielaudio.com